10
JanReact vs. Angular Popularity: Which is Easy to Learn in 2025?
Angular vs React - An Overview
Two of the most widely used JavaScript tools for front-end development are Angular and React. Both of them are strong, have lots of support, and are actively being cultivated in their respective communities. In this article, we'll compare Angular and React in-depth to explore how they match and differ in several important areas.
What Is Angular?
Angular, developed and maintained by Google, is a comprehensive and full-fledged front-end web application framework. Released in 2010, it has undergone significant changes over the years, with the latest version being Angular 12 at the time of writing.
Angular is a TypeScript-based framework that follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) architecture. Developers use HTML as a template language and HTML syntaxes for building single-page client application components.
What Is React?
React also known as ReactJS or React.js is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It was created by Facebook and is currently maintained by both Facebook and a community of individual developers. React was introduced in 2013 and is known for its simplicity and flexibility.
Read More - Angular Interview Questions for Experienced
follows a component-based architecture, allowing developers to build reusable UI components. It is commonly used to create user interfaces for single-page applications from isolated components. It can handle web and mobile apps’ view layers. Thus, React supports web and mobile app development.
Consider our:
Angular vs React: A Detailed Comparison
1. Performance

| Performance in Angular | Performance in React |
| Angular is generally considered to be quite fast. This is partly because of the use of the AOT (Ahead-of-Time) compiler, which compiles your code before it’s sent to the browser, making it faster to load and execute. | Even with Angular’s AoT compiler, React is faster than Angular |
| It uses traditional DOM that updates the whole webpage even with the change of a single element. | It uses the concept of virtual DOM putting less load on the browser. |
| It has bidirectional data binding. Therefore, the more bindings you have, the more watchers are created, and the more cumbersome the process becomes. | Since the data-binding process is unidirectional, bindings are not assigned watchers as in the case of Angular. |
2. Flexibility
| Flexibility in Angular | Flexibility in React |
| Angular is an opinionated framework and provides a lot of built-in features out of the box. | React is very flexible and allows developers to do whatever they want with the code. |
| Angular offers a wide range of options like templates, custom directives, and components for customizing the code and adapting it to a project’s needs. | Here developers have a lot of freedom to create custom components and tailor their code to their project’s needs. |
| This can be limiting if we want to do something that’s either not supported or not clearly defined. | It can be overwhelming because there are so many options and decisions to make. |
3. Essential Tools

| Purpose | Tools in Angular | Tools in React |
| Code editing | VS Code, Sublime Text, Aptana, etc. | VS Code, Sublime Text, and Atom |
| Project setup | Angular CLI | Create React apps (CLI) |
| Server-side rendering | Angular Universal | Next.js framework |
| Testing | Jasmine, Protractor, and Karma | Jest, Enzyme, etc. |
4. App Structure
| App Structure in Angular | App Structure in React |
| The structure of Angular is fixed and complex | The structure of React provides developers with the freedom to choose. There is no “the only right structure” for a React app. |
| Angular is based on three layers – Model, Controller, and View. | React offers only the View layer, while Model and Controller are added with the usage of other libraries. |
5. Learning Curve

| Learning Curve for Angular | Learning Curve for React |
| Angular is a complete MVC framework. | React is a library and not a framework. |
| Knowledge of TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript is a must to learn Angular. | It doesn’t require mastering JavaScript. It is simple to understand if you are familiar with the language |
| Angular is more complex to understand, there is a lot of unnecessary syntax, and component management is intricate. | React is minimalistic: no dependency injection, no classic templates, no overly complicated features. Hence, easy for beginners. |
6. Dependency Injection (DI)
| Dependency Injection in Angular | Dependency Injection in React |
| Angular supports dependency injection accommodating flexibility in both testing and debugging. | React does not fully support dependency injection as it does not fully comply with the idea of functional programming and data immutability. |
| It works through Dependency Injection Containers, Providers, Injection Tokens and Injectors | It takes place through props and children. |
Example of Dependency Injection in Angular
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
import { HEROES } from './mock-heroes';
@Injectable({
// we declare that this service should be created
// by the root application injector.
providedIn: 'root',
})
export class HeroService {
getHeroes() { return HEROES; }
}
Example of Dependency Injection in React
import React from 'react';
import { ApiService } from './services/ApiService';
// Child component that consumes the ApiService
function ChildComponent({ apiService }) {
// Use the injected ApiService
// ...
}
// Intermediate component that passes the ApiService through props
function IntermediateComponent({ apiService }) {
return ;
}
// Parent component that creates the ApiService and passes it through props
function ParentComponent() {
const apiService = new ApiService();
return ;
}
export default ParentComponent;
Here, The ParentComponent creates an instance of the ApiService and passes it through props to the IntermediateComponent. Then, the IntermediateComponent passes it further down to the ChildComponent.
7. Data Binding
| Data Binding in Angular | Data Binding in React |
| Angular uses two-way data binding, also known as bidirectional data binding. Therefore if you change something in the UI, it also reflates at the other end in a component class. | React uses unidirectional data binding. A unidirectional data binding indicates a one-way parent-to-child data flow. Therefore, you can’t trace it backward. |
| It’s a comparatively slower process | It’s a comparatively faster process |
Implementing Data Binding in Angular
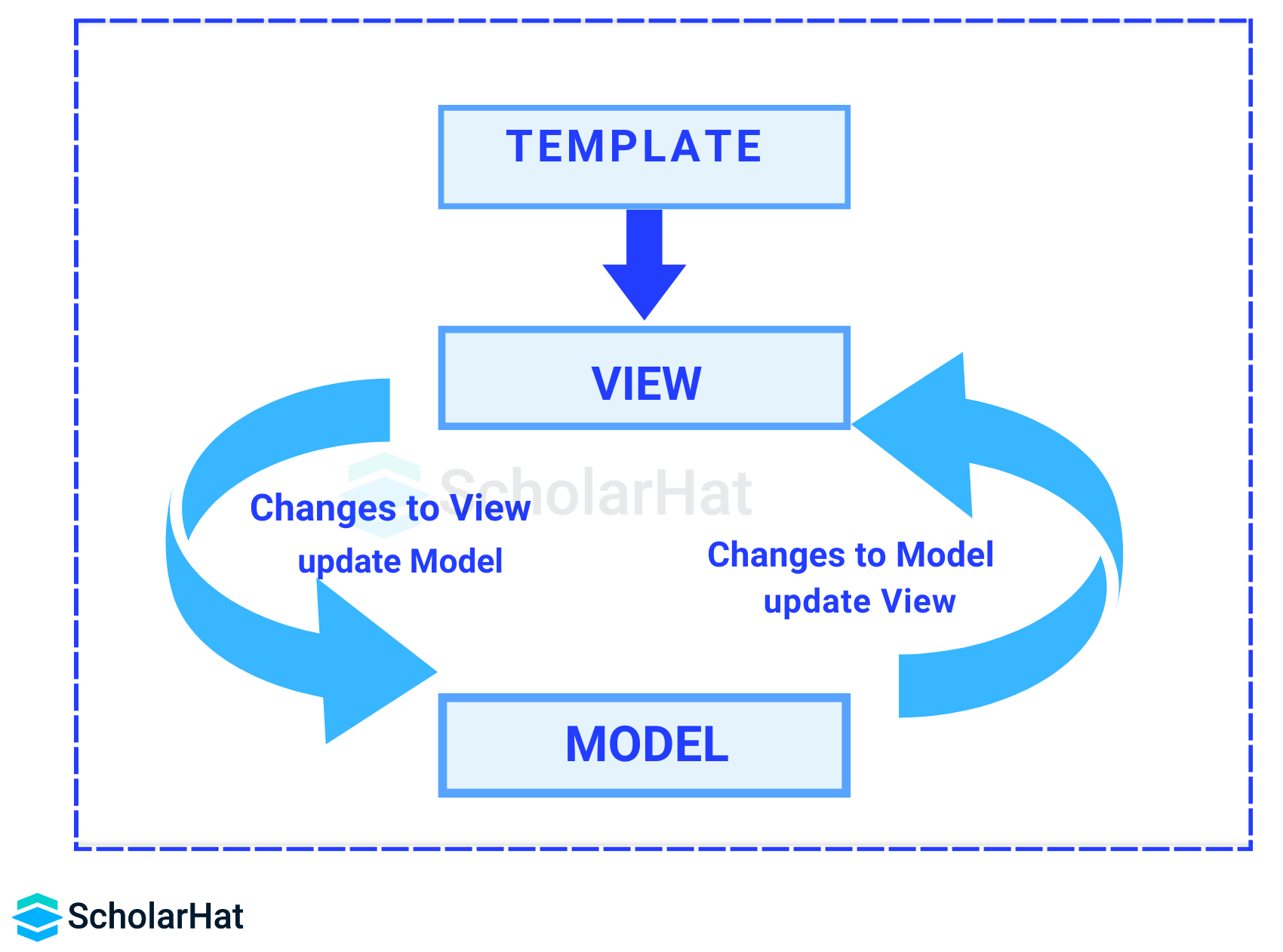
- Interpolation or String Interpolation
// Component Class export class AppComponent { title = 'ScholarHat'; }<!-- HTML Template --><h1>{{ title }}</h1> - Property Binding
// Component Class export class AppComponent { imageUrl = 'path/to/image.jpg'; }<!-- HTML Template --><img [src]="imageUrl" /> - Event Binding
// Component Class export class AppComponent { onClick() { console.log('Button clicked!'); } }<!-- HTML Template --><button (click)="onClick()">Click me</button>
Implementing Data Binding in React
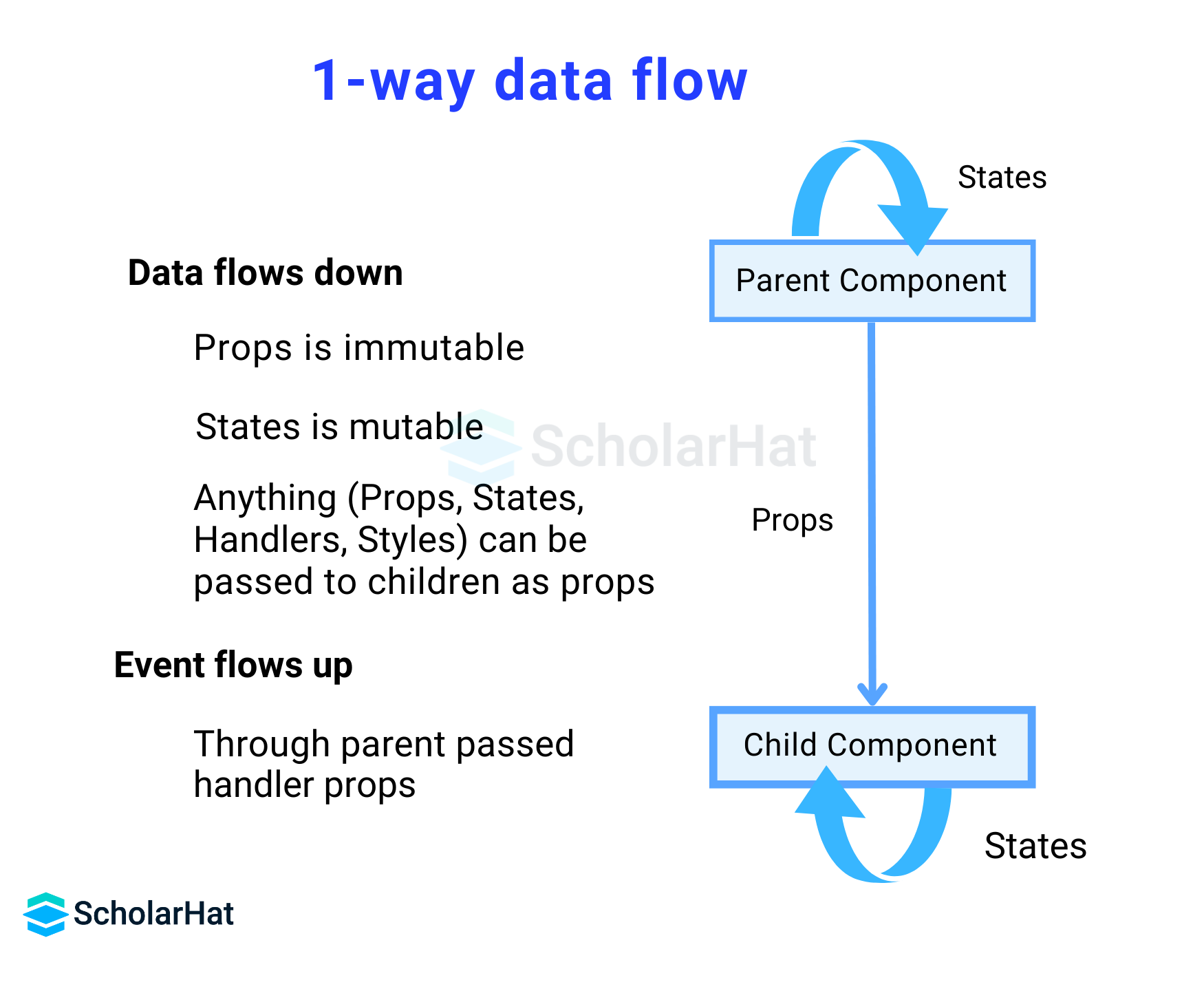
- State
- Class Components
import React, { Component } from 'react'; class MyComponent extends Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { message: 'ScholarHat' }; } render() { return <div>{this.state.message}</div>; } } export default MyComponent; - Functional Components with Hooks (useState)
import React, { useState } from 'react'; function MyComponent() { const [message, setMessage] = useState('ScholarHat'); return <div>{message}</div>; } export default MyComponent;
- Class Components
- Props
- Parent Component
import React from 'react'; import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent'; function ParentComponent() { return <ChildComponent message="ScholarHat" />; } export default ParentComponent; - Child Component
import React from 'react'; function ChildComponent(props) { return <div>{props.message}</div>; } export default ChildComponent;
- Parent Component
- Event Handling
import React, { useState } from 'react'; function MyComponent() { const [count, setCount] = useState(0); const handleIncrement = () => { setCount(count + 1); }; return ( <div> <p>Count: {count}</p> <button onClick={handleIncrement}>Increment</button> </div> ); } export default MyComponent;
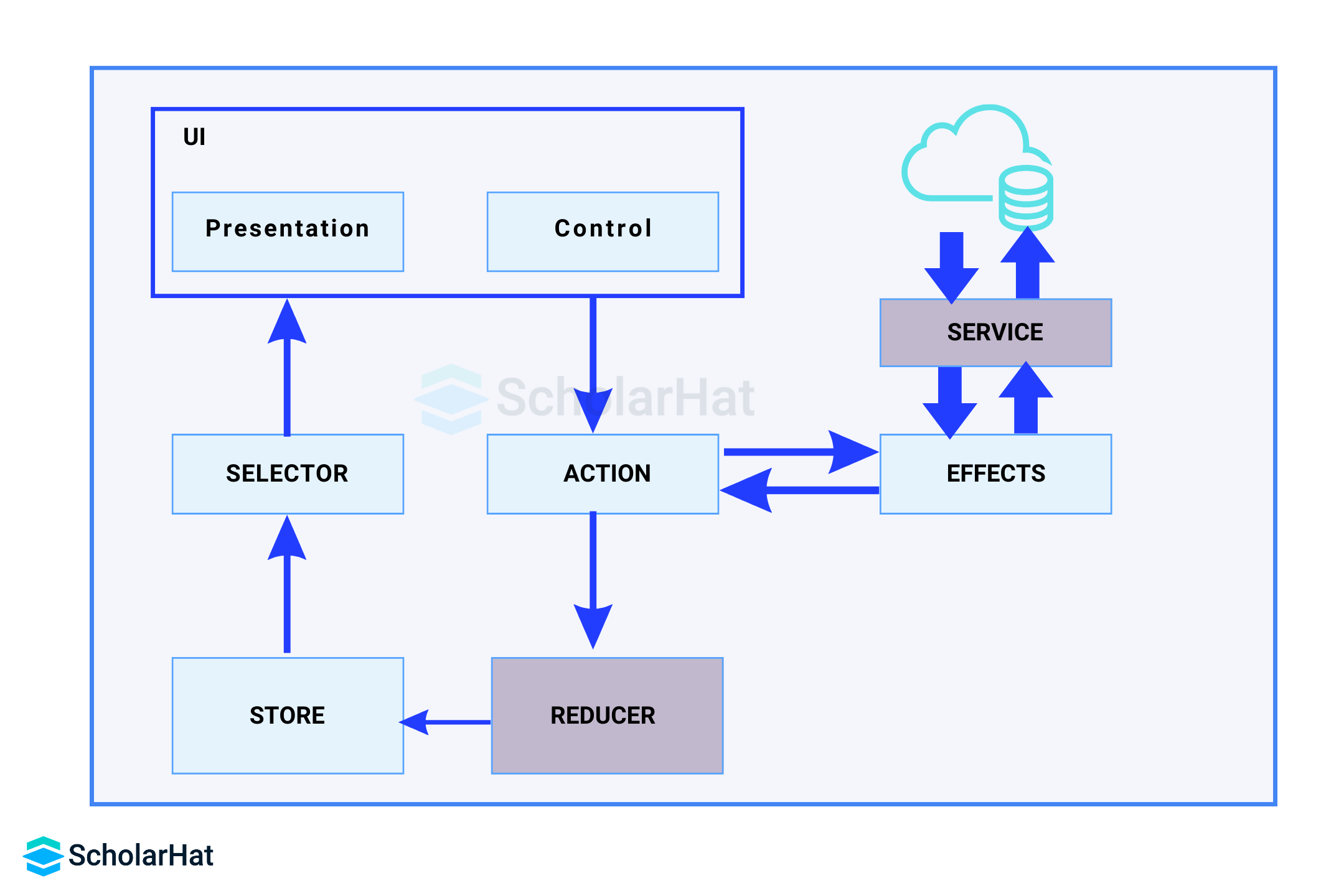
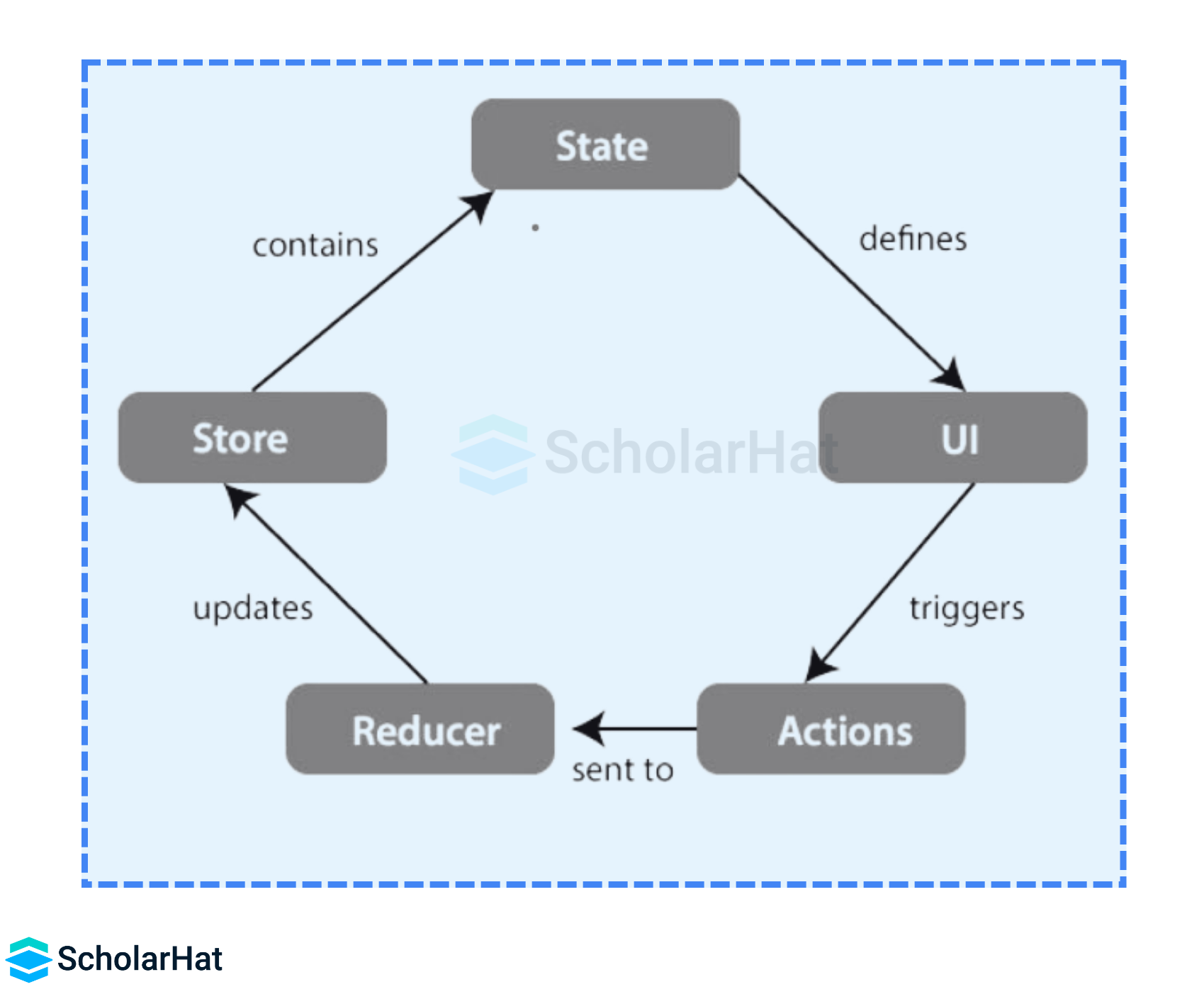
8. State Management
State management is crucial for building scalable applications.
| State Management in Angular | State Management in React |
| NGRX is a state management library, which permits the use of reactive state management. | Generally, REDUX works as a state management library for React. |
| In Angular, component data is stored in component properties. Parent components pass data through to children. | In React, every React component can have a state, so it’s necessary to manage the states of these components separately. |
Example of State Management in Angular
export class HeroListComponent implements OnInit {
heroes: Hero[];
selectedHero: Hero;
constructor(private service: HeroService) { }
ngOnInit() {
this.heroes = this.service.getHeroes();
}
selectHero(hero: Hero) { this.selectedHero = hero; }
}
Example of State Management in React
class Clock extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {date: new Date()};
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Hello world!</h1>
<h2>Now is {this.state.date.toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
);
}
}
9. UI Components
| Angular | React |
| Angular has a built-in Material toolset, and it offers a variety of pre-built material design components. | UI tools for React are developed by the community. There are a lot of free and paid UI components on the React portal. |
| UI configuration becomes simpler and faster due to this. | To use material design components in React, you would have to install an additional library – Material-UI Library & Dependencies. |
10. Industry Trends
| Parameters | Angular | React |
| Market Trends | It is becoming popular day by day but less than React | Its popularity is increasing much faster with time |
| Job Trends | The average annual salary of an Angular Developer in India is around Rs. 4+ lpa | The average annual salary of a React Developer in India is around Rs. 7+ lpa |
Read More:
11. Adoption and Application
| Angular | React |
| MNC Companies previously worked in C, C++, Java use it as it's easy to shift. | Startup companies use it in high demand. |
| Angular is used by Google, Apple, Nike, McD, Upwork, Sony, etc. | React is endlessly used by Facebook, Twitter, Netflix, Instagram, Airbnb, etc. |
12. Community and Documentation
| Community and Documentation Support for Angular | Community and Documentation Support for React |
| Angular is less adopted than React despite being released earlier. | React framework is one of the most popular JS frameworks worldwide |
| Comparatively smaller community support than React | A large community of individual developers and companies |
| Angular has an extensive official documentation | lack of documentation at times |
Angular vs React: When to Use Each?
Use Angular when:
- Building large-scale enterprise applications.
- A comprehensive framework with built-in solutions for various aspects of development is preferred.
- A strong emphasis on TypeScript and a structured, opinionated approach is desired.
Use React when:
- Building smaller to medium-sized applications.
- Flexibility to choose additional libraries and tools based on project requirements is important.
- A more straightforward learning curve is desired, especially for those new to front-end development.
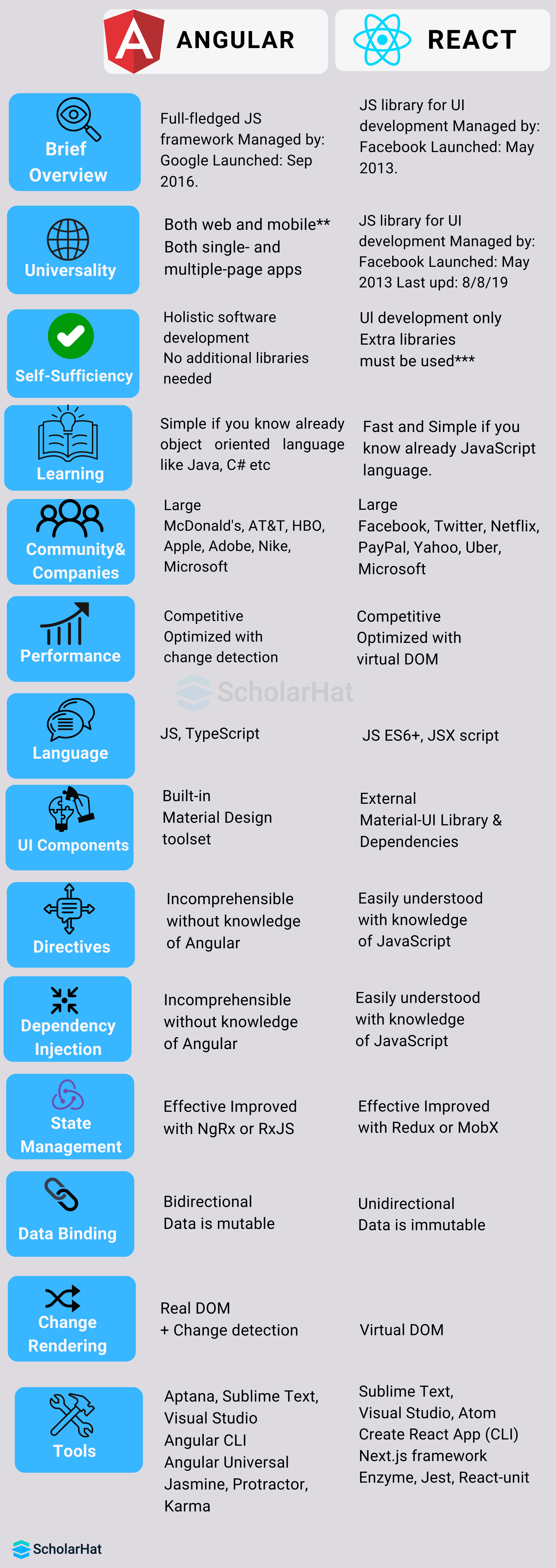
Comparison in a Nutshell
Read More:
Summary
In conclusion, the choice between Angular and React depends on the specific needs of a project and the preferences of the development team. Angular is a robust framework that provides a complete solution for large-scale applications, while React offers flexibility and simplicity, making it suitable for a wide range of projects.
Ultimately, both frameworks have their strengths and weaknesses, and the decision should be based on factors such as project size, complexity, and the team's familiarity with the technology.
FAQs
Take our Angular skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.